Shopware Dictionary
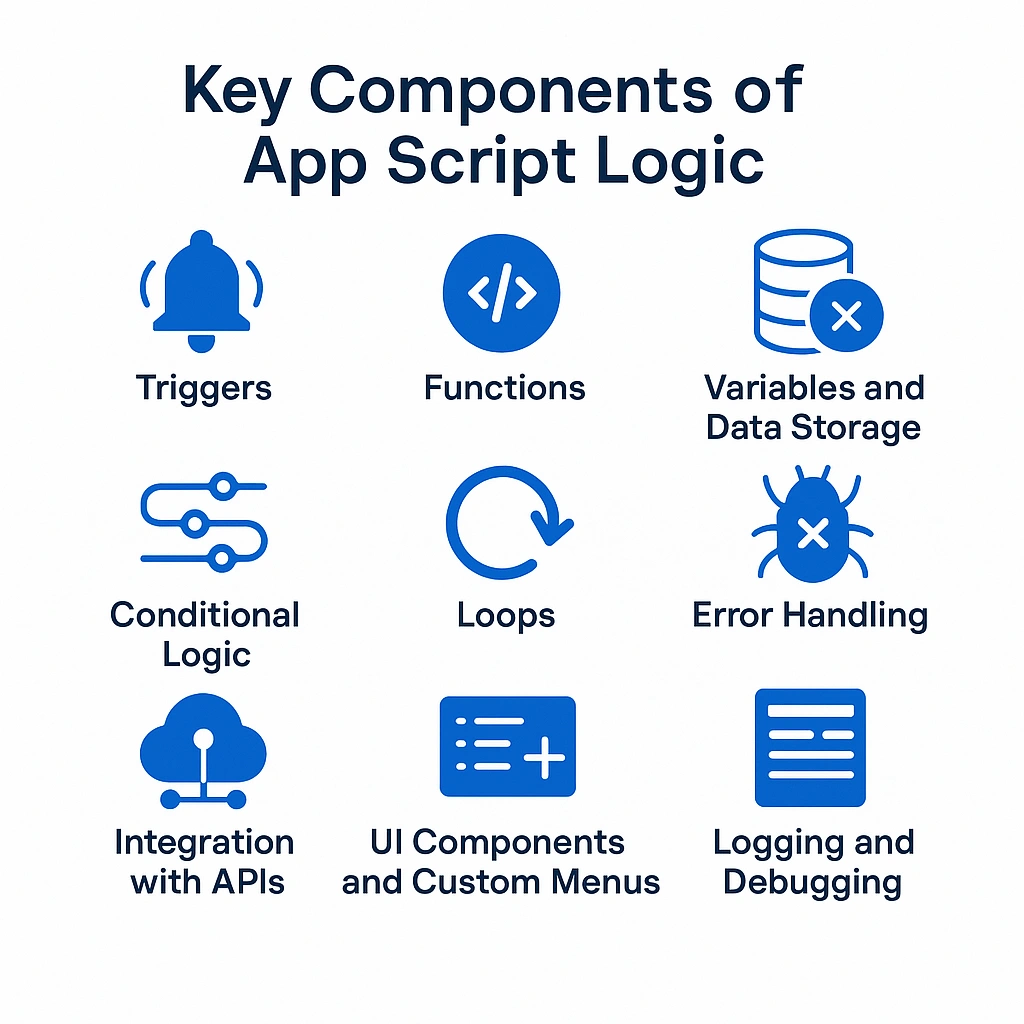
App Script – Logic Specific to Cloud Apps
In today’s digital first world, businesses are increasingly shifting their operations to the cloud. From data storage to customer communication, cloud applications have become the backbone of modern organizations, offering flexibility, scalability, and efficiency that traditional software simply cannot match.