Acces Token- Key for API succes
In the digital era, where platforms, applications, and services constantly exchange information, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have become the glue that holds modern systems together.

In the digital era, where platforms, applications, and services constantly exchange information, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have become the glue that holds modern systems together.

Free 15 min initial consultation directly with our experts.
From e-commerce transactions and payment gateways to social media integrations and AI-powered tools, APIs allow different technologies to talk to each other efficiently. However, with this seamless connectivity comes a significant challenge: security. How can we ensure that only the right people, apps, and systems can access sensitive data or perform specific actions? This is where access tokens step in as the unsung heroes of API success.
An access token is essentially a digital pass a unique, time-limited string of data that proves the identity of the requester and their permissions. When a client (such as a mobile app or web service) wants to interact with an API, it must present a valid token. Without it, the API will simply refuse to respond or grant access. This mechanism prevents unauthorized requests, safeguards user data, and ensures that the API’s resources are only available to legitimate users or systems.
In short, access tokens are not just about granting access; they’re about granting controlled access. They define who can do what and for how long. When implemented correctly, they form the backbone of secure API communication enabling innovation while keeping data safe.
solution25 helps businesses implement secure access token strategies to protect APIs while ensuring smooth and reliable communication between systems. With tailored solutions, solution25 strengthens data security and drives API success through controlled, scalable access management.
The process of using an access token in API communication starts with authentication. Before any token is issued, the user or application must prove their identity often via login credentials, API keys, or more advanced methods like OAuth authorization. Once verified, the authentication server generates an access token and returns it to the requesting client.
This token is then included in every API request, usually in the HTTP header. When the API receives the request, it checks the token’s validity, expiration time, and associated permissions. If all checks pass, the API processes the request and returns the response. If the token is invalid or expired, the API denies access and may request re-authentication.
Tokens can be short lived (enhancing security by limiting exposure time) or long lived (reducing the need for frequent re authentication). In many systems, short lived tokens are paired with refresh tokens, which can request new access tokens without requiring the user to log in again.
By enforcing token-based communication, APIs maintain a strict security protocol while allowing smooth and efficient interactions. This balance between accessibility and security is what makes access tokens a cornerstone of API success.
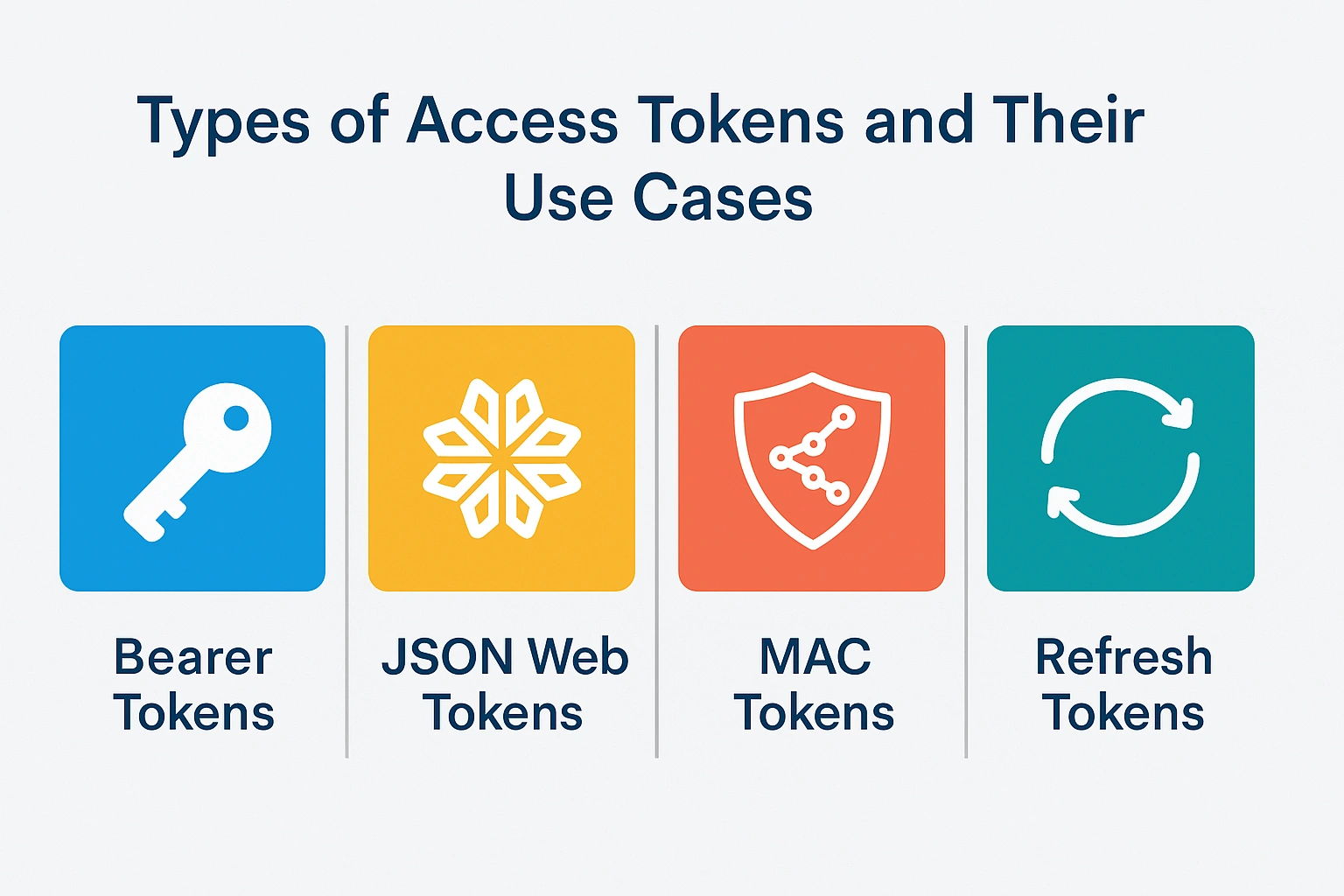
Access tokens come in different formats and serve varied purposes depending on the architecture, security requirements, and integration needs of the API. Understanding these types helps developers and businesses select the right method for their systems.
1. Bearer Tokens
Bearer tokens are the most common type used in modern APIs. They are simple to implement and use, typically included in the HTTP header as Authorization: Bearer . If the token is valid, access is granted without additional verification. While they are convenient, bearer tokens require secure transport protocols like HTTPS to prevent interception, since anyone possessing the token can use it.
2. JSON Web Tokens (JWTs)
JWTs have become a popular choice due to their self-contained nature. A JWT is a compact, URL-safe token that includes encoded JSON data about the user and their permissions, along with a digital signature to prevent tampering. APIs can validate JWTs without contacting the authentication server each time, improving performance. JWTs are often used in large, distributed systems where efficiency is essential.
3. MAC Tokens
Message Authentication Code (MAC) tokens go a step further by requiring cryptographic signing of requests. This ensures not only that the token is valid but also that the request itself has not been altered in transit. MAC tokens are more secure but also more complex to implement.
4. Refresh Tokens
Refresh tokens are not used directly to access resources. Instead, they are used to obtain new access tokens once the old ones expire. This approach minimizes risk while maintaining user convenience. Refresh tokens are typically long-lived but must be securely stored.
Access tokens are powerful, and with great power comes the responsibility to manage them securely. A poorly protected token can become a direct line to sensitive systems, making token security a top priority for API-driven platforms.
1. Use HTTPS Everywhere
Tokens must only be transmitted over secure channels. Even the most robust token can be compromised if sent over plain HTTP.
2. Set Appropriate Expiry Times
Short-lived tokens reduce the window of opportunity for misuse. For higher security, combine them with refresh tokens to maintain usability.
3. Store Tokens Securely
On the client side, tokens should never be stored in insecure places such as local storage in a browser without encryption. Mobile and desktop apps should use secure storage APIs provided by the OS.
4. Implement Token Revocation
A robust system should allow immediate invalidation of compromised tokens. Revocation endpoints help security teams react to suspicious activity without waiting for token expiry.
5. Scope and Limit Permissions
Tokens should only grant the minimal permissions required for a task. This principle of least privilege limits potential damage if a token is leaked.
6. Monitor Token Usage
Continuous monitoring of API calls can reveal abnormal token usage patterns such as requests from unusual locations allowing proactive security measures.
7. Avoid Long Lived Bearer Tokens
Bearer tokens are especially vulnerable because possession equals access. Reducing their lifespan minimizes risk.
Security best practices ensure that access tokens remain a tool for enabling secure communication rather than becoming a point of vulnerability. By combining strong technical measures with proactive monitoring, organizations can build trust in their API ecosystem and prevent costly breaches.
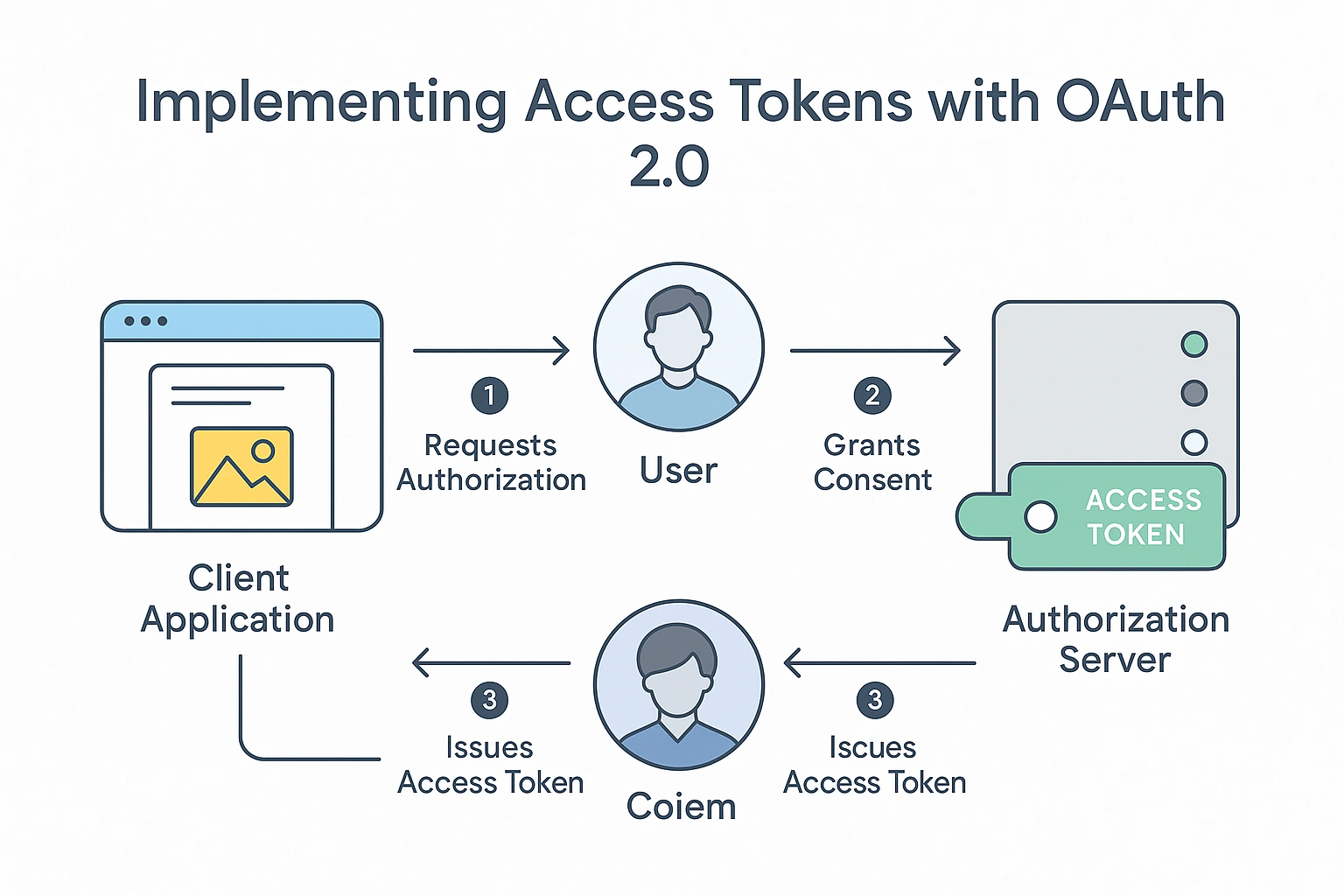
OAuth 2.0 is the industry standard framework for securing API access, and access tokens are at its core. Rather than asking a user to provide a password to every application, OAuth 2.0 issues an access token that represents the user’s permission for the app to act on their behalf.
The OAuth flow typically begins when a client application requests authorization. The user logs in with the authentication provider (such as Google, Facebook, or a company’s own identity system) and grants consent. Once approved, the server issues an access token sometimes along with a refresh token to the client.
There are several OAuth 2.0 grant types, each suited to different use cases:
Authorization Code Grant: Ideal for web and mobile apps where tokens are exchanged securely on the server side.
Client Credentials Grant: Used for machine-to-machine communication where no user interaction is involved.
Implicit Grant: Now considered outdated, but historically used for browser-based apps without a backend.
Device Code Grant: Useful for devices without a browser, like smart TVs.
OAuth 2.0 also supports scopes, which limit what the access token can do. For example, a scope of read:user would allow reading user data but not modifying it. This principle of minimal privilege enhances security.
By combining OAuth 2.0 with best practices like short lived tokens, encrypted transport, and permission scoping, developers can build secure, scalable, and user friendly systems that work across devices and platforms.
Access tokens power a wide range of digital services, from everyday consumer apps to mission critical enterprise platforms.
In social media, tokens enable third-party apps to post updates, fetch profile data, or analyze engagement without the user handing over their password. Facebook’s Graph API and Twitter’s API both rely on tokens for secure, granular access.
In payment processing, services like Stripe or PayPal issue tokens to ensure that sensitive card details never pass through merchant servers. Instead, tokens represent a transaction session securely.
In e-commerce platforms, tokens allow integration between storefronts, inventory systems, and marketing automation tools. For example, a Shopify app can use access tokens to update stock levels in real-time without re-authentication.
In healthcare, tokens secure access to sensitive patient data under HIPAA compliance rules. APIs can enforce strict scope limitations so that an app may view lab results but not edit medical records.
Even in IoT ecosystems, tokens authenticate smart devices with cloud platforms. Whether controlling a smart thermostat or a factory robot, tokens ensure that only authorized devices and users can interact with the system.
Tokens are not just a technical detail they are an enabler of modern, connected services. Without them, the digital experiences we take for granted would be far more fragmented and less secure.
While access tokens streamline API authentication, they come with challenges that can impact security, performance, and usability.
1. Token Theft: If an attacker gains possession of a token, they can access the associated resources. Using HTTPS, short expiration times, and secure storage helps mitigate this risk.
2. Token Expiration Issues: Expired tokens can interrupt services if refresh tokens are not properly implemented. Developers should ensure seamless token renewal to maintain smooth user experiences.
3. Token Revocation: Not all systems allow immediate revocation. Implementing a revocation endpoint is essential for responding to breaches quickly.
4. Token Bloat in JWTs: While JWTs are powerful, packing too much data can lead to performance issues, especially if tokens are sent with every request. Keeping payloads lean is crucial.
5. Scope Mismanagement: Overly broad scopes increase security risk, while overly restrictive scopes frustrate users. A balance must be struck based on actual use cases.
6. Cross-Origin Requests (CORS): When APIs are accessed from browsers, incorrect CORS settings can block legitimate requests or open security holes.
By anticipating these challenges and implementing robust solutions, businesses can ensure that their access token strategy supports both security and performance goals.
As technology evolves, access tokens will continue to adapt to new security and integration requirements.
Zero Trust Architectures are gaining momentum, requiring re-validation of every access request. In such setups, tokens may become shorter-lived and more tightly scoped than ever before.
Decentralized Identity (DID) systems are also emerging, where tokens could be issued by blockchain-based identity providers. This could enable more privacy-respecting authentication without centralized data storage.
AI-driven security monitoring may analyze token usage patterns to automatically detect anomalies, such as tokens used from multiple locations within seconds.
IoT growth will drive the need for ultra-lightweight, low-power token systems that still maintain strong security.
In short, while the concept of an access token remains the same granting controlled access the ways they are issued, validated, and monitored will continue to evolve alongside the digital ecosystem. Organizations that keep pace with these trends will maintain a secure and competitive edge.
An access token is only as secure as the practices surrounding its creation, storage, and transmission. Because tokens act like digital keys, losing them or allowing them to be intercepted can be as damaging as handing over a physical key to an intruder.
One of the most important security principles is using HTTPS for all API communication. Without encryption, tokens sent over the network can be intercepted via man in the middle (MITM) attacks. TLS ensures that the token remains confidential during transit.
Token expiration is another critical safeguard. Short lived tokens reduce the window of opportunity for attackers. For long running sessions, use refresh tokens instead of issuing perpetual access tokens. This way, even if a token is stolen, it quickly becomes useless.
Secure storage is equally important. In browser environments, tokens should be stored in HTTP-only cookies rather than localStorage, reducing exposure to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. In server side applications, tokens should be kept in encrypted databases or secure key vaults.
Scope limitation ensures tokens have only the permissions they truly need. This principle of least privilege minimizes potential damage if a token is compromised. For example, a token that can only read customer orders should not be able to delete them.
Finally, organizations should monitor token usage through logging and anomaly detection. Sudden spikes in API calls or requests from unusual IP addresses could indicate misuse. Proactive m
While all three access tokens, API keys, and session cookies facilitate authentication and authorization, they serve different purposes and have different strengths.
API keys are static identifiers, often tied to the application rather than the user. They’re simple to implement but less secure if exposed, since they typically do not expire. API keys work well for server to server communication in low risk environments but are less suited for scenarios involving sensitive user data.
Access tokens, on the other hand, are dynamic and short lived. They are often issued after authentication and carry specific scopes, making them ideal for granular access control. They integrate seamlessly with modern protocols like OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect.
Session cookies are common in traditional web applications. They store a session ID that the server uses to retrieve the user’s state. While cookies are convenient, they require careful handling to prevent cross-site request forgery (CSRF) and XSS attacks.
In modern API-driven architectures, access tokens offer the most flexible and secure approach, particularly for mobile and single page applications where server-based sessions are impractical. However, many systems use a combination for example, a web app might use cookies for browser sessions and access tokens for mobile app authentication.
While security is often the first topic in access token discussions, developer experience is equally important. APIs should be easy to integrate, and access tokens can simplify this process.
Instead of handling complex user authentication for every request, developers can rely on a single issued token until it expires. This reduces repetitive code, speeds up development, and minimizes authentication related bugs.
Access tokens also standardize authentication across different services. A developer integrating with multiple APIs say, a payment gateway, CRM, and analytics platform can use similar token-based flows for all, making onboarding faster.
With JSON Web Tokens (JWTs), tokens can also carry claims (like user roles or subscription tiers), allowing developers to implement authorization logic without making extra API calls to fetch user data. This not only improves efficiency but also reduces latency.
From a testing perspective, tokens allow easy simulation of different user roles and permissions by generating tokens with various scopes. This is particularly helpful in staging environments, where developers need to replicate real-world scenarios without affecting production systems.
Ultimately, access tokens bridge the gap between strong security and developer friendly APIs, enabling innovation without sacrificing safety.
Shopware’s flexibility allows it to integrate with a wide range of automation tools, enabling businesses to streamline processes, reduce manual work, and improve operational efficiency. Popular solutions like Pipedream Shopware integration, Tray.io Shopware integration, and Parabola Shopware integration offer no-code and low-code approaches for connecting Shopware with third-party apps. More advanced options like Shopware Integromat automation, Shopware Airtable automation, and Shopware with Hugging Face enable both structured data workflows and AI-powered features.
For AI-driven personalization and intelligent commerce, integrations such as Shopware with OpenAI, Shopware LangChain automation, Shopware with AutoGPT, and Shopware with ChatGPT provide advanced natural language and decision-making capabilities. Businesses can also explore Shopware GPT integration for custom AI assistants and Shopware Python automation or Shopware JavaScript automation for tailored, code driven workflows.
When speed and efficiency matter, Shopware AI tools, Shopware API automation tools, and Shopware webhook automation ensure real-time data exchange. Companies can leverage low-code tools Shopware or no-code automation Shopware to implement rapid changes without heavy development cycles, making workflow automation Shopware accessible to both technical and non-technical teams.
Beyond basic integrations, Shopware supports a robust ecosystem of AI orchestration tools and advanced workflow builders. Businesses can use Shopware with Retool, Shopware with Node-RED, Shopware with Prefect, Shopware with Temporal, and Shopware with Apache Airflow for complex data pipeline management. Enterprise grade automation platforms like Shopware with Microsoft Power Automate, Shopware with Google Cloud Workflows, and Shopware with AWS Step Functions allow seamless cross system coordination.
For process-heavy environments, Shopware with Automation Anywhere, Shopware with UIPath, and Shopware with IBM Watson Orchestrate enable robotic process automation (RPA) and intelligent task execution. This positions Shopware as a Shopware automation platform capable of handling Shopware event-driven workflows and Shopware workflow builder tools for both synchronous and Shopware background job automation.
AI-powered Shopware async processing AI ensures scalable performance under heavy load, while a Shopware AI integration platform supports innovation with a composable automation Shopware approach. Dataheavy organizations benefit from Shopware data pipeline tools and a complete Shopware process automation stack, ensuring every part of the business from inventory updates to marketing campaigns is efficiently connected and optimized.
In today’s fast moving digital economy, the difference between thriving and struggling often lies in how well a business can adapt, scale, and innovate. Modern e-commerce platforms offer incredible flexibility, but without the right approach to integration, automation, and data flow, even the most feature-rich systems can fall short of their potential. The key lies in creating a well-orchestrated ecosystem where processes work together seamlessly, decisions are made with precision, and customer experiences are consistently exceptional.
This level of efficiency is not achieved by accident it requires both vision and execution. Businesses must be willing to look beyond traditional setups, embracing advanced automation capabilities and leveraging the tools that best suit their operational needs. When systems communicate effortlessly, repetitive tasks vanish, and insights become actionable in real time, companies can redirect their focus to strategic growth, innovation, and relationship building.
However, technology alone is not enough. Success also depends on having a trusted partner who understands not only the tools but also the business goals behind them. That’s where a team like solution25 becomes invaluable. Their expertise bridges the gap between complex technical possibilities and practical business outcomes, ensuring that every implementation delivers measurable value. By guiding companies through the process from planning to execution they help businesses create scalable, future proof systems that truly work for them.