
The main distinction between these two design job roles is in their characteristics.
 They design a user interface prototype. Furthermore, they track user behavior through various testing methods such as email surveys and A/B testing. Product designers, on the other hand, usually create the overall feel and look of the product. They provide information about the functions of various parts of the product. Furthermore, they identify a market scope and develop plans for applying the solution to the issues.
They design a user interface prototype. Furthermore, they track user behavior through various testing methods such as email surveys and A/B testing. Product designers, on the other hand, usually create the overall feel and look of the product. They provide information about the functions of various parts of the product. Furthermore, they identify a market scope and develop plans for applying the solution to the issues. 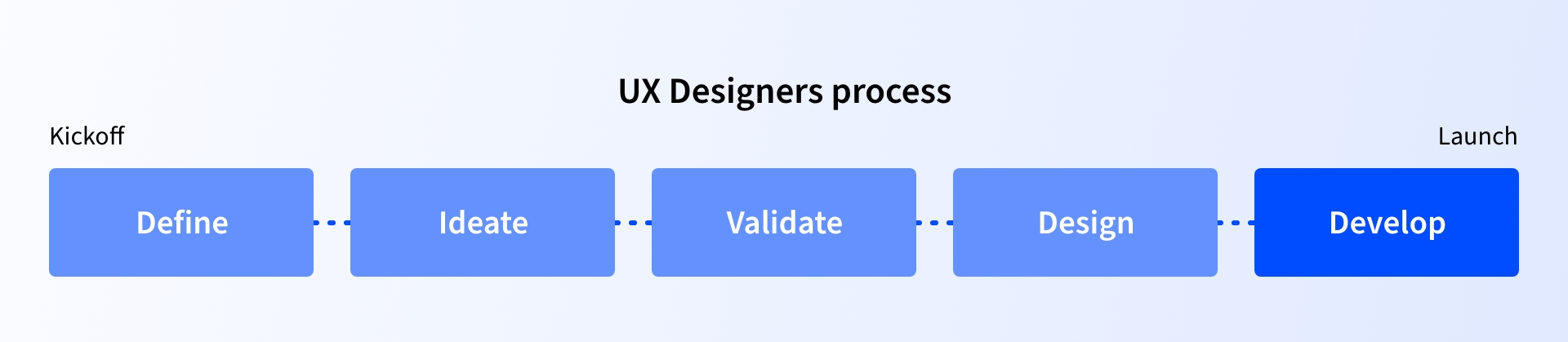 In addition, a product designer should be curious. They must be logical and analytical thinkers. A product designer must have a strategic mindset because they work with planning and design. In a nutshell, they should be well-versed in the market and the product.
In addition, a product designer should be curious. They must be logical and analytical thinkers. A product designer must have a strategic mindset because they work with planning and design. In a nutshell, they should be well-versed in the market and the product.